Diseases are disruptions in homeostasis that effect the body, causing it to become "off-balanced" and act differently then when healthy. After learning about the many parts and purposes of the immune system, we will continue onto the diseases that, if they do happen to pass through the skin, mouth, cilia and "fortress wall" of the immune system, effect the body.
Diseases
Primary Immunodeficiency
A disease that infects from childhood onward. The disease can not be a result of another disease, drug treatment or exposure to toxins. Meaning it is mostly from genetic disorders. This disease weakens the immune system, allowing infections to occur more easily. If you are born with primary immunodeficiency, you usually are missing some of the immune system defense. Forms can be rare and not noticed until adulthood, or very severe and can be discover as soon as a baby is born. When untreated, damage to organs and/or disabilities can occur. Symptoms can include:
▪ Frequent ear infections, meningitis, bronchitis, or sinus infections
▪ Blood infections
▪ Inflammation of liver
▪ Auto immune disorders
▪ Low platelet count
▪ Diarrhea
▪ Delayed development
Unlike acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, primary immunodeficiency
can not be spread from one person who is infected to another. People with PID
have an increased risk of cancer. Around 1 in 500 people are born with PID.
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)
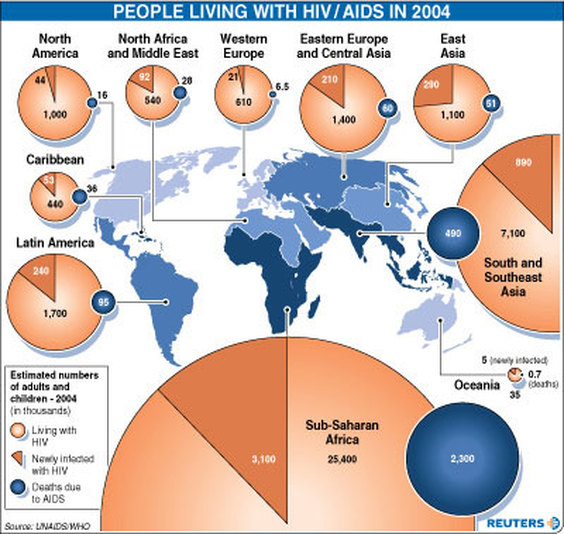
AIDS is an incurable disease caused by infections with HIV. Over time, AIDS destroys your immune system, making it impossible to fight off the smallest infections. HIV can develop into AIDS. AIDS is commonly spread by sexual content but can be spread with contact of blood of a human who has AIDS, for example blood transfusions. AIDS can also be spread from a mother to her baby child during pregnancy if the mother has AIDS. There are usually no early signs or symptoms which can be like the flu, but they will go away for months or sometimes years. In 2007 it was estimated that 34 million people live with AIDS worldwide. AIDS kills an average of 2 million people a year, and 300,000 are children. Over ¾ of the deaths were in Africa.
▪ Frequent ear infections, meningitis, bronchitis, or sinus infections
▪ Blood infections
▪ Inflammation of liver
▪ Auto immune disorders
▪ Low platelet count
▪ Diarrhea
▪ Delayed development
Unlike acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, primary immunodeficiency
can not be spread from one person who is infected to another. People with PID
have an increased risk of cancer. Around 1 in 500 people are born with PID.
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)
AIDS is an incurable disease caused by infections with HIV. Over time, AIDS destroys your immune system, making it impossible to fight off the smallest infections. HIV can develop into AIDS. AIDS is commonly spread by sexual content but can be spread with contact of blood of a human who has AIDS, for example blood transfusions. AIDS can also be spread from a mother to her baby child during pregnancy if the mother has AIDS. There are usually no early signs or symptoms which can be like the flu, but they will go away for months or sometimes years. In 2007 it was estimated that 34 million people live with AIDS worldwide. AIDS kills an average of 2 million people a year, and 300,000 are children. Over ¾ of the deaths were in Africa.